
Hard to ignore facts about Crawl Budget and its impact on SEO
Google follows three basic steps to generate SERPs from websites: crawling, indexing, and ranking. The crawling process begins with crawlers or bots discovering publicly available web pages using links on the sites, analyzing the content of each page, indexing the stored information, and ranking the website. Therefore, when a user searches for a query, the most relevant results are displayed. Without an effective crawling process, the websites would not be visible in SERPs. Now, let us learn in-depth about the crawl budget and the best practices for crawl optimization.
Crawl budget sometimes referred to as crawl time, is assigned by search engines to each website to prioritize their crawling efforts across millions of websites. The two factors that affect a website’s crawl budget are crawl rate limit and crawl demand.
Crawl rate limit or host load is defined as maximum requests per second Googlebot makes when crawling your site. We essentially have two aspects regarding the crawl rate – crawl capacity: how much the Googlebot can crawl from a server. Crawl capacity is usually tied more to the technical aspects of the server, which includes how quickly a server responds to the requests or do we see a lot of errors. The other aspect is crawl demand: how much we want the bots to crawl from the server.
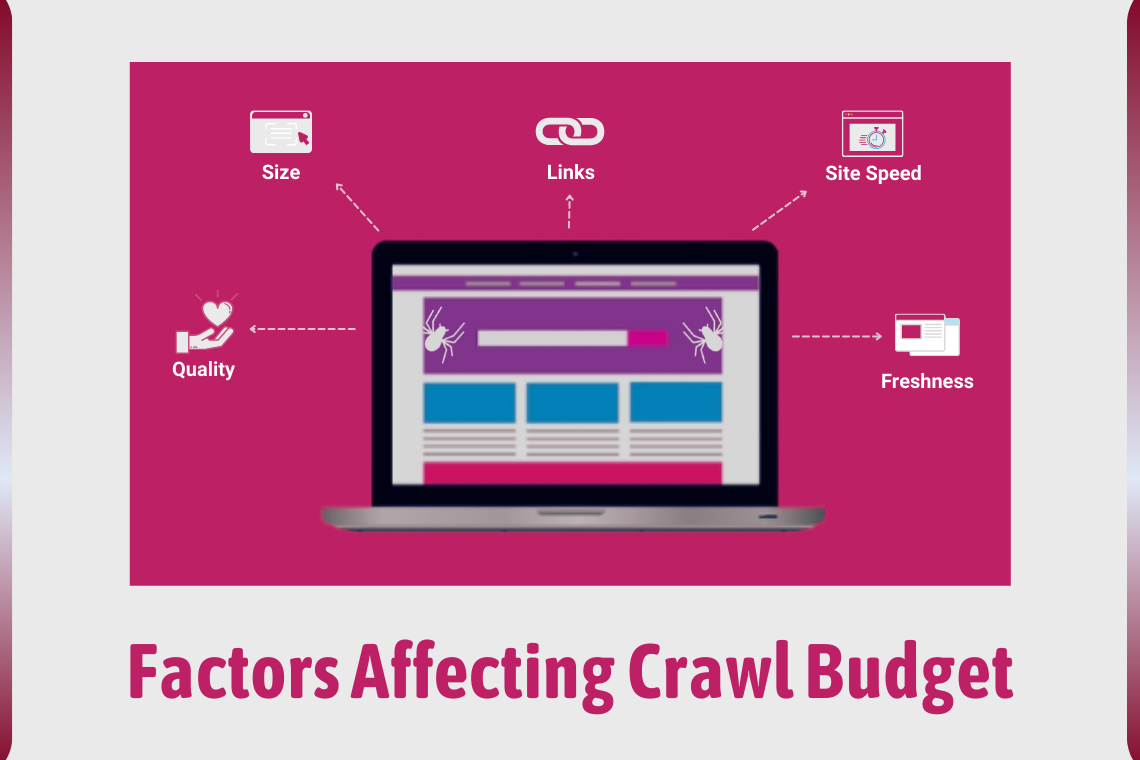
The crawl budget is distinct for every website, and a site’s crawl budget is determined automatically by Google by weighing the crawl rate limit and crawl demand. The search engine uses various factors to allocate the crawl budget to a particular site. In general, the main factors that are considered are:
Size – Bigger websites with a large number of pages will require more crawl budget than smaller websites.
Links – how many internal links, external and broken links on the site.
Site speed – Well-optimized sites get a different budget than slower sites with server errors.
Freshness – Google will prioritize content based on how often the pages are updated.
Quality – Googlebot will automatically limit its budget if the content quality is poor.
How can crawl budget optimization impact your SEO? Optimization of crawl budget means getting search engines to spend more time on your website wisely. So, it is the process of helping search engines crawl and index more of the important content of your website. Here are some tips to optimize the crawl budget, like improving the popularity and refreshing the site’s stale content; Improving page load time and helping search engines find important content faster; Preventing bots from crawling non-canonical URLs; Updating the website’s crawl rate limit by logging in to Google Search Console because high crawl rate may also put too much stress on the server; Improve crawl capacity by making sure that the server is as fast as possible.
Thus, this shows that the crawl budget affects SEO in many regards, such as improving crawl can benefit the website traffic, ranking, and revenue. However, an increased crawl rate alone will not necessarily lead to better rankings in search results.
CONCLUSION
The crawl budget is the summation of crawl demand and crawl rate limit. Simply an increased crawl rate will not help you rank better if your content is not up to quality.
So, now that you have significant knowledge of concepts of the crawl budget make sure you fix any issues and optimize the crawl budget accordingly to help your website flourish.
To watch the latest Google SEO Office Hours, please check out the video below:

Durga
About The Author…
Durga has a master’s degree in engineering. Technological advances in digital space interest her a lot. Digital marketing is her forte and she passionately follows latest trends in the digital marketing space. She has written many trending articles on various social media platforms. Her areas of interest include SEO Optimization, structured data, SMM, Keywords research and analysis etc. She is focused, resourceful and dedicated.


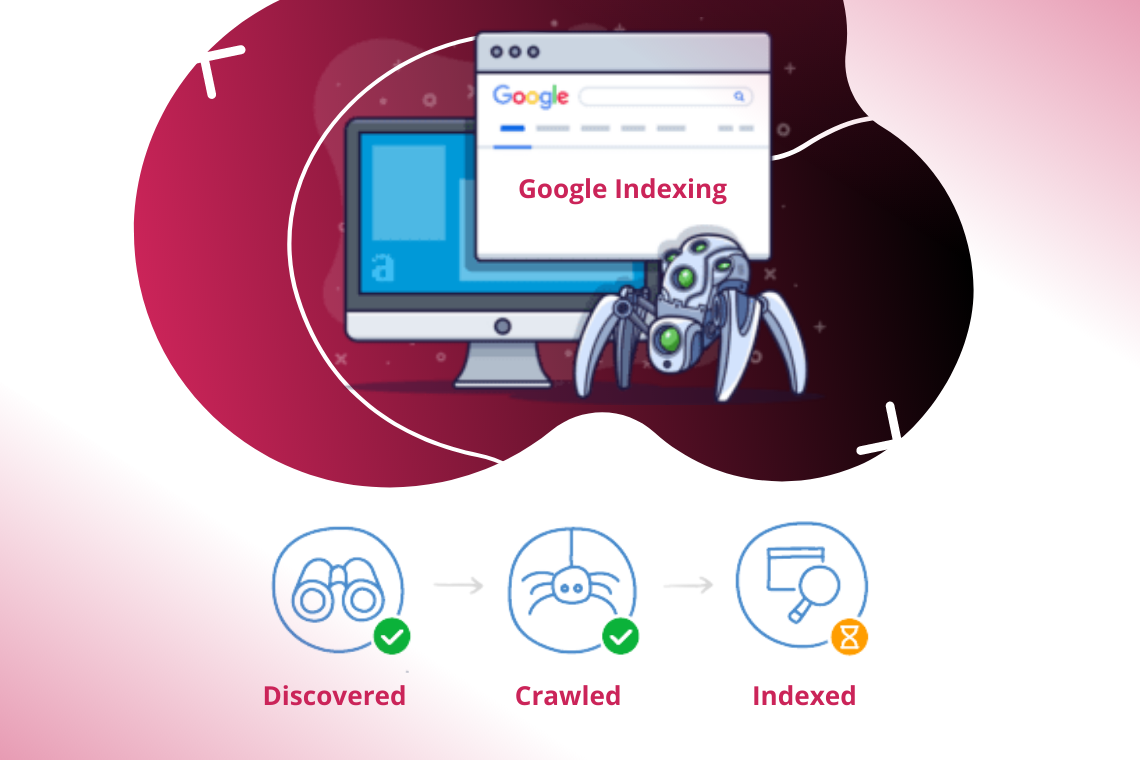 Lack of value – Google’s algorithm decides not to index a specific page if it understands that a particular page or your website is not important to show in search results for users. Still, it might re-evaluate the page next time it crawls again.
Lack of value – Google’s algorithm decides not to index a specific page if it understands that a particular page or your website is not important to show in search results for users. Still, it might re-evaluate the page next time it crawls again.
 1.
1. 




